News& Information
-
Medical Trends
 Home -> News& Information -> Medical Trends
Home -> News& Information -> Medical Trends
3.8 Women's Day | Women's Health Guide
She is a mother, wife, daughter, and a powerhouse in the workplace, as well as a warm harbor at home. Yet, in the midst of their busy lives, many women often neglect their own health.
On the occasion of International Women’s Day on March 8th, International Medical Center-Beijing is launching a special women’s health management package that focuses on prevalent diseases and health risks among women, providing professional care to protect the vitality of every woman.
01
Thyroid Diseases:
The “Balancer” of Emotion and Metabolism

The thyroid is a key endocrine organ that regulates energy and metabolism throughout the body. Currently, there are over 200 million individuals in China affected by thyroid diseases. In developed regions, about 90% of thyroid cancers are discovered through health screenings, especially among women of reproductive age, and include conditions such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and thyroid nodules.
Prevention Tips:
1. Maintain a balanced iodine intake by consuming iodine-rich foods.
2. Monitor any changes in neck lumps and seek medical attention if abnormalities occur.
3. Include thyroid function and structural assessments in regular check-ups, particularly for pregnant women and those entering menopause, as the incidence of thyroid disease increases during these periods.
02
Anemia
Anemia is a condition caused by various factors that result in a lower-than-normal number of red blood cells or hemoglobin levels in the blood. Approximately 20% of the population in China is affected, with women, children, and the elderly being particularly vulnerable. Chronic anemia can lead to fatigue, dizziness, and impaired organ function and immunity, making prevention crucial.
Prevention Tips:
1. Maintain a balanced diet rich in iron, such as beef and liver, alongside vitamin C-rich fruits like oranges and kiwis to enhance iron absorption, while ensuring adequate protein intake from lean meats and eggs.
2. Establish a regular sleep schedule, ensuring 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
3. Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly, such as brisk walking or jogging, combined with strength training.
4. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to prevent negative impacts on nutrient absorption and the hematopoietic system.
03
Caring for Ovarian Health
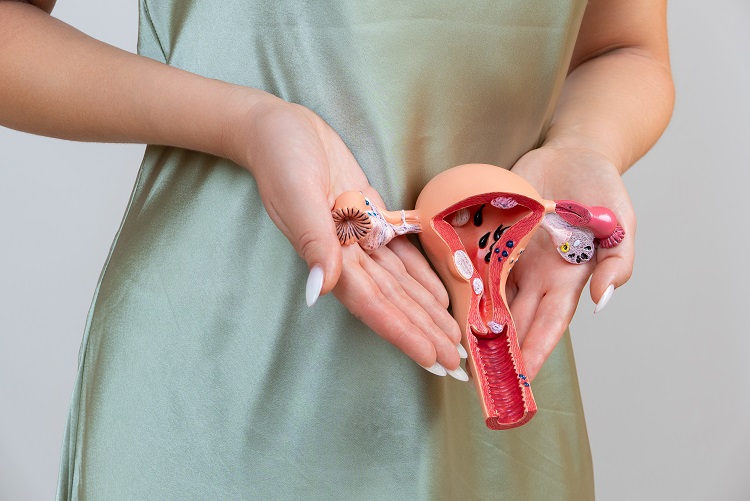
1. Decreased Ovarian Reserve and Premature Ovarian Failure (POF)
Premature ovarian failure refers to the decline in ovarian function before the age of 40, presenting as amenorrhea, decreased estrogen levels, and infertility.
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) has become a key indicator in assessing ovarian reserve. It is secreted by ovarian follicles and directly reflects a woman's egg count, serving as a critical marker for predicting fertility potential and the risk of early ovarian failure.
Prevention Tips:
1. Follow an antioxidant-rich diet to combat oxidative damage.
- Recommended foods include dark vegetables (spinach, broccoli), berries (blueberries, cranberries), nuts (walnuts, almonds), and foods high in vitamins C and E (citrus fruits, avocados).
2. Supplement with key nutrients:
- Vitamin D: Regulates ovarian hormone secretion and improves egg quality (sources: sunlight, fatty fish, fortified milk).
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduce inflammation and balance hormone levels (sources: salmon, flaxseeds, chia seeds).
- Folate: Supports DNA repair and reduces the risk of premature ovarian failure (sources: leafy greens, legumes, whole grains).
3. Avoid high-sugar and high-fat diets:
- Long-term consumption of refined sugars and trans fats (e.g., milk tea, fried foods) can lead to insulin resistance and chronic inflammation, indirectly harming ovarian function.
2、Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is an endocrine metabolic disorder affecting women’s reproductive health, primarily characterized by irregular menstruation, hyperandrogenism, and cystic changes in the ovaries.
Prevention Tips:
1. Lifestyle adjustments: Maintain a balanced diet, reduce sugar intake, and avoid obesity, as weight gain exacerbates PCOS symptoms. Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and decrease androgen levels.
2. Regular check-ups: Periodic gynecological exams can promptly identify menstrual irregularities and ovulation issues, especially for women with a family history of PCOS.
3. Psychological well-being: Reducing stress and ensuring sufficient sleep while maintaining a positive mindset can help in balancing hormones.
04
Ensuring Breast Health:

Prevention of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies in women and its incidence is rising globally. Here are some prevention recommendations:
1. Self-examination: Conduct monthly breast self-exams to familiarize yourself with your breast structure. If you notice lumps, changes in skin texture, or discharge, seek medical advice promptly (self-examination is not a substitute for professional screenings).
How to perform a self-exam?
- Stand in front of a mirror and observe both breasts for size symmetry, color changes, and whether the nipples are aligned. Check for skin dimpling or changes in vessels.
- Use a systematic palpation technique, alternating hands, and applying gentle pressure to avoid misidentifying glandular tissue as lumps.
- Follow a clockwise sequence to check each quadrant of the breast, starting with the upper inner quadrant and moving around to the nipple.
2. Regular screenings: Women over 40 should undergo annual breast ultrasounds and mammography screenings (frequency may vary based on local screening guidelines).
3. Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight, exercise moderately, limit alcohol intake, avoid smoking, and consume a diet rich in antioxidants from fruits and vegetables.
05
Preventing Cervical Changes:
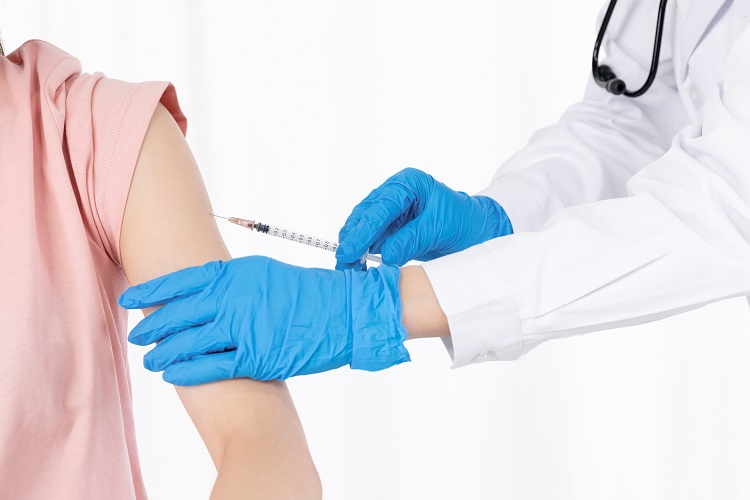
Cervical Cancer Prevention
Cervical cancer poses a significant threat as one of the leading malignancies in women globally; however, it can be effectively prevented through screenings and vaccinations.
1. Vaccination: HPV vaccines can prevent high-risk HPV infections and significantly reduce the risk of cervical cancer. Adhere to immunization schedules during the appropriate age brackets.
2. Regular screenings: Adult women should undergo regular Pap smears (TCT) or HPV tests to detect cervical dysplasia early and facilitate timely intervention.
3. Good personal hygiene: Maintain vaginal health and use protective measures to reduce the risk of HPV infection.
06
Osteoporosis:
The "Silent Bone Killer" After Menopause

Osteoporosis is an insidious "killer" of bone health, affecting approximately one-third of women over 50 in China as aging progresses. It weakens bones, making fractures from minor accidents common and severely impacting quality of life.
Prevention Tips:
1. Dietary changes: Increase calcium intake through foods like milk, tofu, and shrimp, combined with vitamin D-rich options (like salmon) or adequate sun exposure to enhance calcium absorption, while ensuring sufficient protein intake to maintain bone strength.
2. Regular exercise: Engage in at least 30 minutes of brisk walking daily, or running 3-4 times a week, while also performing weight-bearing exercises to stimulate bone health; use dumbbells for strength training to support bones and perform balance exercises to reduce fall risk.
3. Lifestyle habits: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption (men should not exceed 25 grams daily, women 15 grams) and moderate coffee intake to 3-4 cups per day, while minimizing sugary carbonated beverages. Maintain correct posture when sitting, standing, and walking is also essential.
4. Regular screenings: Women aged 45 and above, and men over 50, should have their bone density checked annually, especially high-risk individuals who should increase the frequency of assessments for early detection and intervention.