News& Information
-
Medical Trends
 Home -> News& Information -> Medical Trends
Home -> News& Information -> Medical Trends
Type 1 Diabetes-What you should know
Basics about Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but usually is
diagnosed in children and adolescents and it appears at two noticeable peaks.
The first peak occurs in children between 4 and 7 years old, and the second is
in children between 10 and 14 years old.

Type 1 diabetes causes the level of sugar in the blood to become high.
The body is not producing enough of a hormone called insulin.
Insulin helps the
sugar to enter the cell and be used from the cell to produce energy. This
hormone has to be replaced with injections or insulin pump in order to keep the
blood sugar levels in the bloodstream under control. Type 1 diabetes symptoms
can come quickly, the child will complain about feeling thirsty, peeing more
than usual particularly at night, loosing weight and experiencing extreme hunger, thrush that keeps coming back,
blurred vision and cuts and grazes that aren’t healing.

Managing Type 1 Diabetes
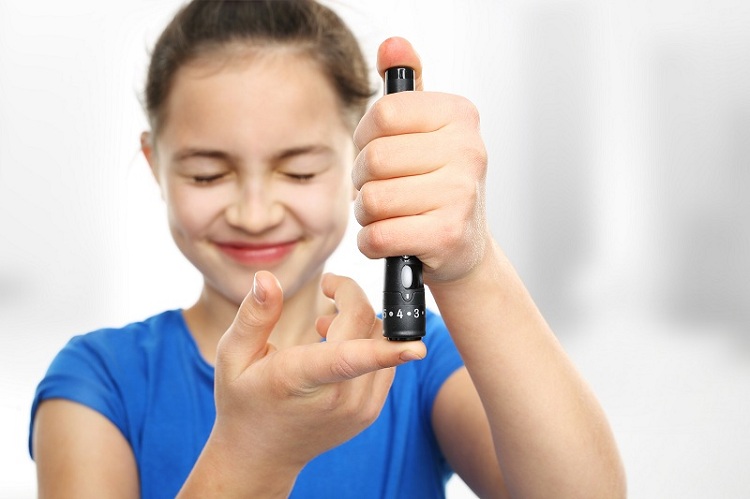
The blood glucose (sugar) levels are affected by meals and exercise that’s why is important to check the blood sugar levels by testing.Checking the blood glucose levels it’s done with a glucose meter.
Best time to check
the blood glucose levels is before meals,2 to 3 hours after meal, before,
during and after exercise and before going to bed.This should help
to have more stable blood glucose levels.
The blood sugar levels can be monitored
continuously by wearing a blood sugar sensor placed under the skin. The sensor
sends data to a transmitter which, in turn, sends it to receiver worn like a
pager.The receiver displays blood glucose levels
on a continuous basis.
If the blood sugar level is too low it can cause seizures and coma.High blood sugar level can be dangerous and cause complications such as kidney damage and kidney failure and damage to the blood vessels of the retina potentially leading to blindness.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
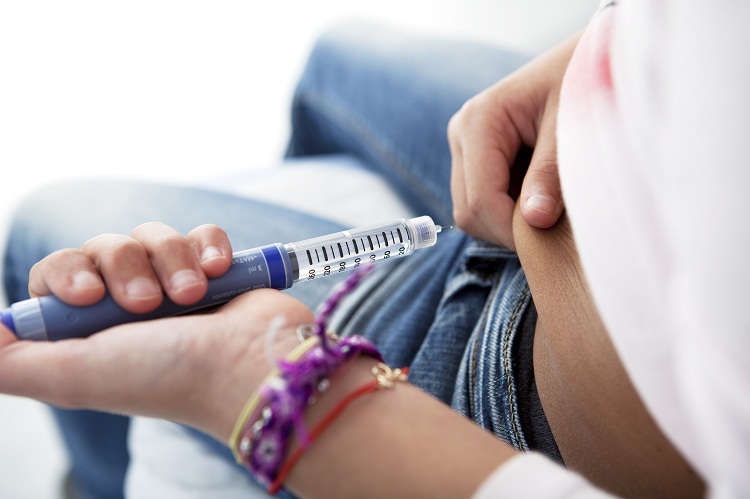
To keep the blood sugar levels under
control insulin has to be replaced with injections or insulin pump. The usual
dose for children is 0.8 to 1 unit/kg/day. Injecting the insulin usually it is
done with insulin pen. This pen has a small needle inside. Injecting insulin
doesn’t usually hurt and the injection is done in the thighs, tummy or
buttocks.

There is a specific diet for the patients
with type 1 diabetes and everyday the calories should be calculated. Half of
the calories 45-60 % should be carbohydrates,10-20% should be proteins and
25-35% lipids.
Type 1 Diabetes Care
The type 1 diabetes
care is lead by pediatric endocrinologist, trained nurse, nutritionist and a
social worker.
The family and the
child work together with the special team to learn all the things they need to
adjust to in order to have a better care for the child having this type of
diagnose.
The diabetes care in kids then in adults is even more challenging because the kids grow, eat different kinds of food and in different amounts.
Regular appointments with the special care
team should be every 1 or 2 weeks at
first and then every 3 months.